Exploring the Fascinating World of Optical Illusions
An optical illusion is a captivating visual phenomenon where the perception of an image doesn’t align with its actual physical properties. In simpler terms, the way you see an image might differ significantly from its true nature. These illusions occur due to how our brain processes and interprets visual information, often leading us to perceive things in ways that don’t match reality.
From seemingly moving objects to colors that appear out of place, optical illusions challenge our perception and provide valuable insights into how our minds work. In this article, we’ll delve into the different types of optical illusions and explore the science behind them.
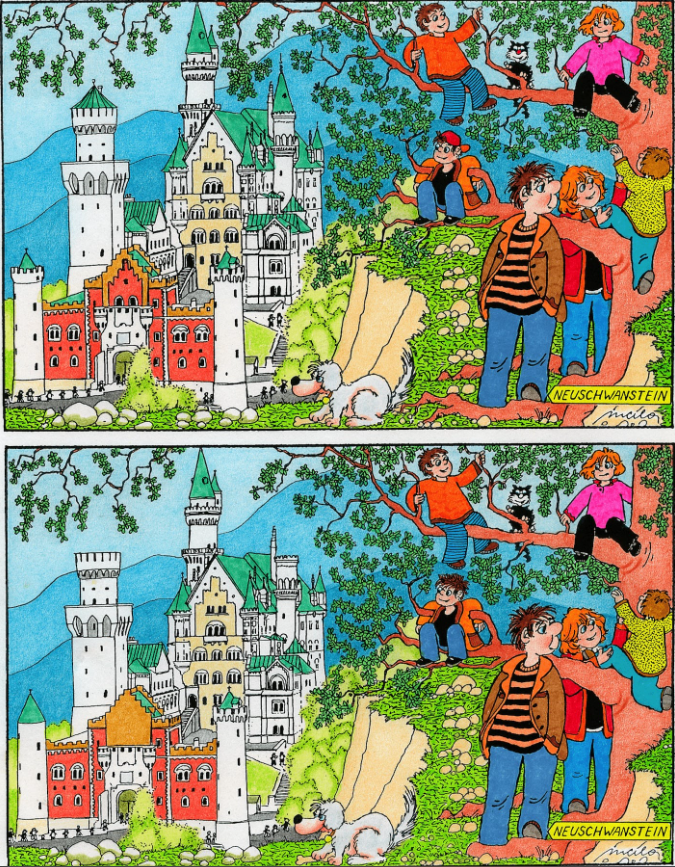

1. Ambiguous Illusions: When Images Have More Than One Meaning
Ambiguous illusions are unique in that they can be interpreted in multiple ways. They leave room for our brains to switch between different perspectives, creating a dynamic and sometimes confusing visual experience.
A famous example is the Necker Cube. This seemingly simple image of a cube can be seen in two different orientations: one facing upward and the other downward. Your brain oscillates between these perspectives, highlighting how perception isn’t always stable.
These illusions make us realize that our brains don’t just passively receive visual data—they actively work to interpret it in different ways based on context and expectation. Ambiguous illusions are a great way to showcase the mind’s flexibility in interpreting reality.
2. Geometrical Illusions: Distorted Shapes and Impossible Objects
Geometrical illusions often involve shapes or structures that seem distorted or out of place. Some of these illusions can even depict objects that appear physically impossible, even though they’re perfectly ordinary from a mathematical standpoint.
One of the most famous examples is the Penrose Triangle, also known as the “impossible triangle.” This optical illusion creates the illusion of a solid, three-dimensional object that could never exist in reality. Despite its apparent physicality, the Penrose Triangle is a visual paradox that tricks the brain into seeing something impossible.
Such illusions challenge our understanding of geometry and spatial relationships. Our brains tend to make sense of shapes based on rules of symmetry and alignment, and these illusions play with those expectations to create something that feels real but defies logical construction.

3. Motion Illusions: Making Still Images Appear to Move
Motion illusions involve static images that give the impression of movement. These illusions take advantage of visual cues and patterns to trick the brain into perceiving motion, even though the image remains still.
The Rotating Snake Illusion is one of the most striking examples of motion illusions. When you look at the image, it seems like the snakes are spinning, but in reality, the image is static. The movement is a trick of the eye caused by the arrangement of color and pattern, which induces a feeling of continuous rotation.
Motion illusions are not only visually mesmerizing, but they also highlight how our brains process motion in dynamic visual environments. These illusions often occur when specific patterns are placed in such a way that our brains expect continuous movement or change.
4. Color Illusions: How Colors Can Trick Our Eyes
Color illusions play with the way colors interact with each other, creating effects that mislead our perception of color, contrast, or brightness. These illusions can make objects appear different colors than they actually are, or cause certain parts of an image to seem more vivid or muted than they should.
An example of this is the Afterimage Illusion, where staring at an image for a prolonged period causes you to see complementary colors when you look away. The famous Checker Shadow Illusion is another example, where two squares of the same color seem different due to the surrounding shadows and light contrasts.
These color illusions reveal how our brains interpret colors based on context and surrounding stimuli. The interaction between different colors can create fascinating effects that often defy the true nature of the colors themselves.

Understanding the Science Behind Optical Illusions
So, why do optical illusions happen? The short answer is that our visual system is complex and not always perfect. When our eyes receive visual information, our brains process it by applying shortcuts based on past experiences, expectations, and the surrounding context. This system usually works well, but sometimes it can be tricked, leading us to see things that aren’t there.
For example, motion illusions occur when our brain anticipates continuous change based on patterns, causing it to perceive motion where none exists. Similarly, geometric illusions manipulate shapes and angles, causing our brains to misinterpret dimensions and alignments.
Color illusions, on the other hand, are linked to the way our brains process light and contrast. The brain uses contextual information to understand how light affects color, but when certain patterns or backgrounds are introduced, it can lead to perceptual errors.
The Fascinating World of Optical Illusions
Optical illusions do more than just entertain—they offer a glimpse into how our brains work and how we interpret the world around us. Whether it’s a twisting triangle that defies geometry or a static image that appears to move, these illusions challenge our understanding of reality and remind us that perception is not always as straightforward as we think.
The study of optical illusions also plays a significant role in psychology and neuroscience. By examining how our brains process visual information, researchers can learn more about perception, cognition, and the underlying neural mechanisms that help us make sense of the world.
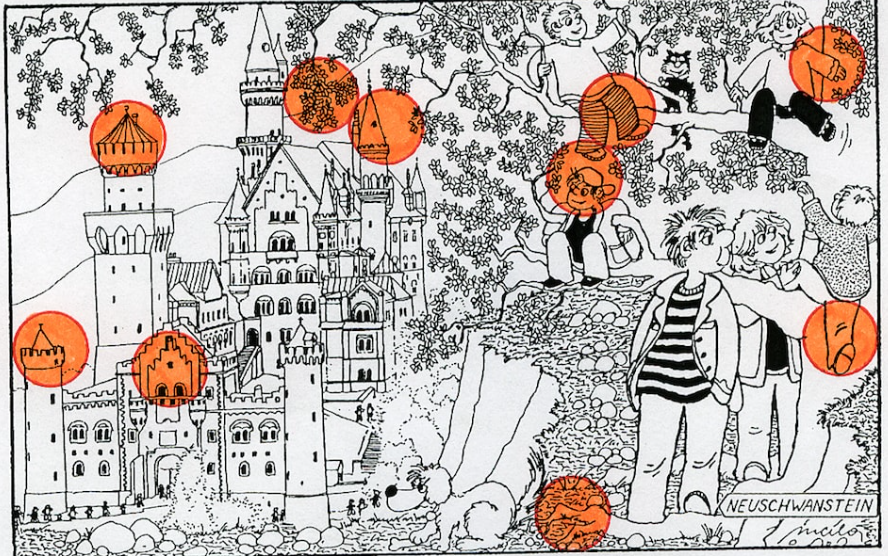

Conclusion: The Mind’s Eye and the Power of Perception
Optical illusions serve as a fun and enlightening reminder that our perceptions are not always accurate reflections of reality. They show us how our brains work to make sense of the world, interpreting images and information in ways that can sometimes be misleading.
Next time you encounter an optical illusion, take a moment to appreciate the complexity of your brain’s processing abilities. These fascinating visuals not only entertain us but also reveal the incredible power and flexibility of the human mind. So, next time you see a Penrose Triangle or a rotating snake, remember—what you see might not always be what’s really there.