Mastering Stream Crossings: How Raccoons Navigate Nature’s Waterways
The Ingenious Raccoon at the Water’s Edge
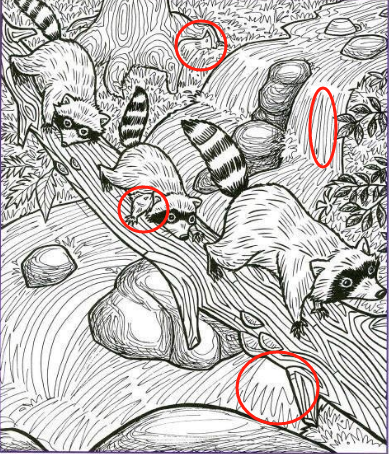
In a sun-dappled forest, a mother raccoon guides her curious kits across a fallen log bridge spanning a gentle creek. Each masked bandit pads carefully, tails lifted for balance, whiskers twitching at the scent of fresh water—and perhaps a fish dinner. This endearing family scene highlights the raccoon’s remarkable adaptability and problem-solving skills, from dexterous paws to keen spatial awareness. Let’s explore the science, behavior, and habitat features that enable these nocturnal foragers to thrive along streams and rivers.

Why Waterways Matter to Raccoons
Raccoons (Procyon lotor) are intimately tied to riparian zones—areas where land and water meet—for several reasons:
- Abundant Food Sources: Crayfish, frogs, fish, aquatic insects, and fallen fruits congregate along stream banks, offering a diverse smorgasbord.
- Safe Travel Corridors: Fallen logs, rocky outcrops, and overhanging roots create natural causeways, allowing raccoons to move between feeding sites while minimizing exposure to predators.
- Home Range Anchors: Many raccoon families establish dens near water, in hollow trees or burrows, ensuring quick access to hydration and food.
- Cooling and Play: During hot months, raccoons often wade, dip paws, and dunk food to soften it—a behavior known as “dousing” that also helps regulate body temperature.
By understanding these ecological drivers, we appreciate the critical role of healthy stream ecosystems in supporting raccoon populations.
Anatomy of a Stream Crossing: Balance, Brains, and Bristles
How do raccoons traverse slippery logs without tumbling into the current? Key adaptations include:
- Highly Sensitive Paws: With up to 50,000 tactile receptors per square centimeter, their front paws detect subtle shifts in texture and water flow, guiding each step.
- Strong Claws: Semi-retractable claws grip rough bark, while webbing between toes provides extra purchase on damp surfaces.
- Low Center of Gravity: Compact bodies and stout limbs keep their center of mass close to the log, reducing wobble.
- Spatial Memory: Raccoons remember safe crossing routes and can retrace them even in darkness, relying on mental maps of their territory.
These combined skills make raccoons consummate stream navigators, even in treacherous rain-slick conditions.

Raccoon Family Dynamics During Water Crossings
Water crossings aren’t solo expeditions—they’re family affairs:
- Lead by Example: The mother raccoon typically goes first, testing each log for stability and safety. Her confident stride signals kits it’s time to follow.
- Teaching Through Observation: Kits watch and learn crossing techniques—how to gauge log width, where to place paws, and when to pause for balance.
- Huddled Encouragement: If a youngster hesitates, the mother emits soft vocalizations or gently nudges it forward, reinforcing confidence.
- Staggered Formation: Kits cross in single file to avoid crowding, each pausing at safe spots before the next advances.
Observing these tender training sessions reveals raccoon intelligence and social cohesion in the wild.

Building Your Own Wildlife-Friendly Waterway
Homeowners with nearby streams can support raccoons—and other woodland creatures—by enhancing riparian habitats:
- Leave Fallen Logs: Resist clearing every downed tree. Decaying wood provides natural bridges, perches, and insect nurseries.
- Plant Native Vegetation: Shrubs, grasses, and canopy trees stabilize banks, offer cover, and supply fruits and nuts for raccoons.
- Create Brush Piles: Small stacks of branches near the water’s edge serve as refuges for insects and amphibians—the very prey raccoons seek.
- Maintain Clean Water: Avoid harsh pesticides and fertilizers that runoff into streams, protecting aquatic life and the entire food chain.
- Respect Quiet Zones: Keep human activity to designated paths. Gentle silence lets wildlife habituate to your presence without stress.
By fostering healthy riparian corridors, you’ll witness more heartwarming scenes of raccoons and their kits mastering nature’s waterways.

Safety and Conservation Considerations
While raccoons are charming, coexistence requires care:
- Avoid Hand-Feeding: Wild diets keep raccoon instincts sharp; hand-feeding can lead to habituation and conflict.
- Secure Trash and Pet Food: Locked containers discourage nighttime raiding and help raccoons forage naturally.
- Protect Den Sites: If you spot a mother and kits near hollow logs, observe from a distance and avoid disturbing dens.
- Support Wetland Preservation: Contribute to local conservation groups working to maintain stream water quality and natural vegetation.
Responsible stewardship ensures both human safety and thriving raccoon populations.
Conclusion: Celebrating Raccoon Resilience by the Stream
Next time you wander along a shaded creek and glimpse the telltale mask of a raccoon, pause to appreciate its incredible mastery of water crossings. From the mother’s cautious lead down a moss-slick log to the kits’ eager yet tentative steps, these scenes embody adaptability, intelligence, and familial bonds in the wild. By nurturing healthy riparian habitats and respecting these nocturnal neighbors, we safeguard the elegant balance that allows raccoons—and countless other creatures—to flourish at the water’s edge.





